One of the major judgements of a reliable industrial material is the mechanical strength. There’re several numeric values to describe the mechanical strength of a material, for example, tensile strength, bending strength, compressive strength and abrasion resistance.
In great many industrial activities, vibration & motion is inevitable. Therefore, abrasion resistance could be a key factor for material durability.

However, for those non-metallic materials yet with good thermal insulation, normally the mechanical strength is not so good. It’s like that you can’t have your cake and eat it.


Fiberglass cloth is one of the most regular high-temperature resistant materials, being widely used in metallurgy, petrochemical, construction etc. It’s made from glass ball, with temperature resistance of 550℃. It obtains a relatively good mechanical strength.
Silica fiber cloth is a material that withstands much higher temperature than fiberglass cloth. That is 1000℃. However, it’s much less durable against abrasion.

To improve the mechanical strength of the silica fiber cloth, we make it coated with silicone rubber. It’s therefore delivered a more durable characteristic (about 50% increase).

From a recent experiment conducted by Hantai Lab, we find out the changes between these two materials under different working temperatures.


● Under 350℃ for 15 minutes, bear load 850 grams, humidity 70%.
● The mechanical strength of fiberglass cloth drops by 85%.
● Silica fiber cloth has a slight change of 5% decrease.


▼ Well, let’s see what happens when the temperature reaches 650℃.

● Under 650℃ for 15 minutes, bear load 850 grams, humidity 70%.
● The mechanical strength of fiberglass cloth drops to 0%.
● Silica fiber cloth experiences a significant drop by 95% which is a little bit unexpected.


▼ Let’ s go to the temperature limit of silica fiber cloth, 1000℃.

● Under 1000℃ for 15 minutes, bear load 850 grams, humidity 70%.
● Silica fiber cloth remains its original form, but the mechanical strength remains only 1%.
● Fiberglass cloth? It’s melted and returns to be its very original ingredient form as a piece of glass.

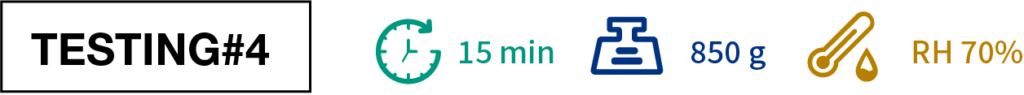
In TESTING#4, we also discover how significantly different thicknesses of the material influence on the mechanical strength under high temperature. A 25% increase in thickness could lead to a mechanical strength remain of 4+ times.

Well, though the materials obtain a nominal temperature resistance, when we put them into use, don’t literally decide it by the temperature numbers, we’d better take the other working conditions into consideration, e.g. vibration, loading pressure, acid, fluid, weathering etc. Because the other conditions could shorten the life of the materials and weaken its actual protection under the high temperature. For sake of safety, we use heavier material at the key spots.




Stay tuned with Hantai and we would love to share more information with you from our experience and experiments. Let’s grow together!